Blockchain Technology and its Potential Applications
Blockchain
Remember the classic ‘snake’ game in the cell phones of the 2000s (or even in YouTube of the slow internet era)? Remember how the snake increases one unit in size for every point it takes? Now consider, that the increase is a record of information, that is secure and can’t be modified and that the snake itself is a chain of records that is ever expanding; each point gained, and the subsequent size increase is an addition of a block to the chain.
(If you are unaware of the game, do read on, the analogy ends there.)
So, what exactly is the Blockchain?
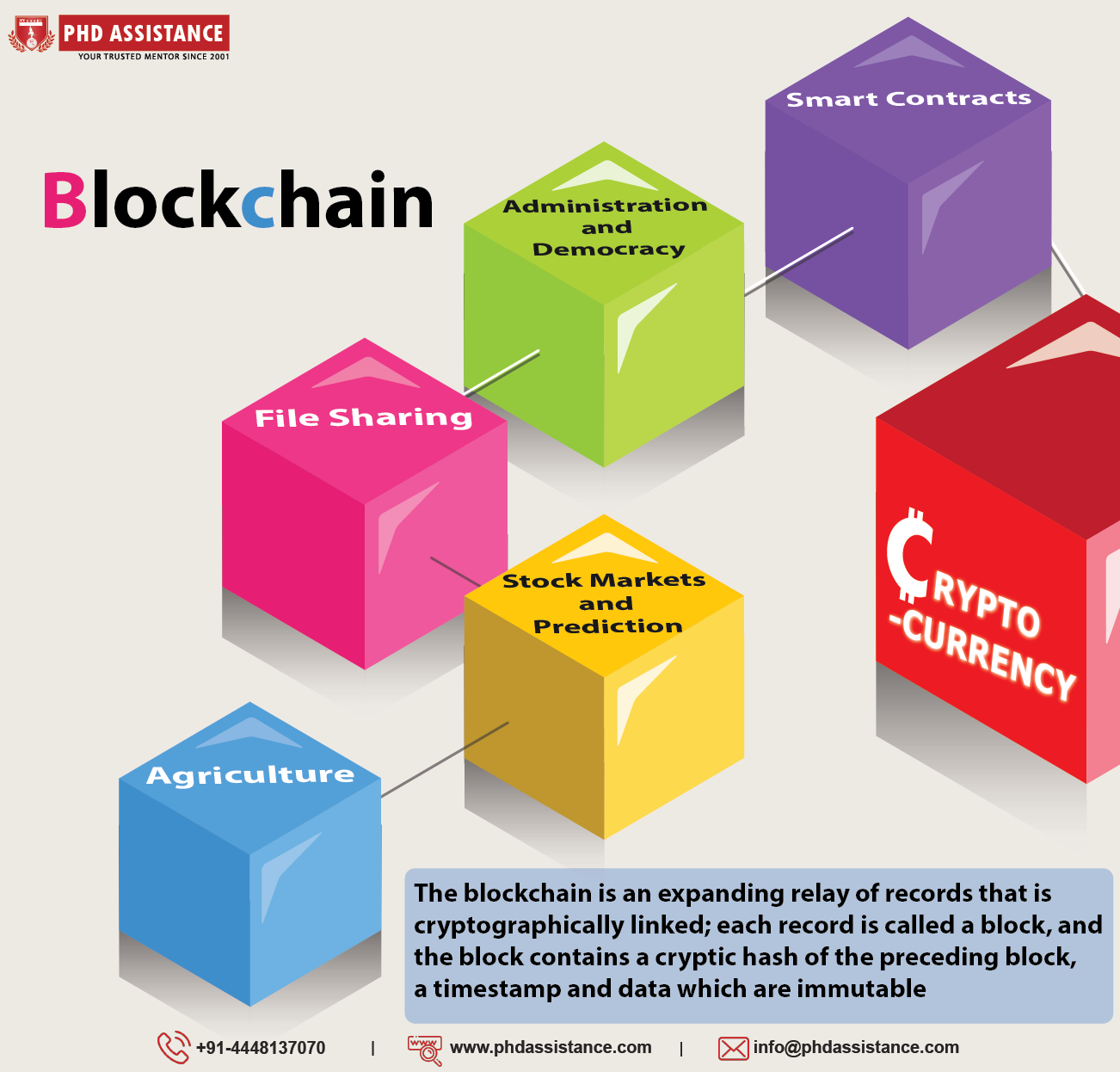
The blockchain is an expanding relay of records that is cryptographically linked; each record is called a block, and the block contains a cryptic hash of the preceding block, a timestamp and data which are immutable. The Blockchain employs a consensual peer-to-peer decentralized network which makes it safe from hacking as there is no central server which can be modified. Devices connected in the network are updated regularly; so, when a block is added to the network, the information is distributed throughout the network. It facilitates a public inspection of the records which can be verified by anyone. The data in a block can’t be altered or modified without altering the subsequent blocks which require the consensus of the network majority; which is theoretically possible but practically improbable. Hence, the Blockchain is safe by design and has a high value in Byzantine fault tolerance.
Why was Blockchain invented?
In digital currencies, there is the problem of double spending where the digital token or currency can be duplicated and used again. The problem can be tackled by a centralized server, but it is prone to hacking. Blockchain was invented to solve this problem without the need for a centralized server by the still-anonymous person or team that goes by the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto for the cryptocurrency Bitcoin. It is a decentralized, open, distributed ledger of public transactions that can be verified by anyone and modified by none. Since its invention, applications of the Blockchain have been expanded and is continued to be researched.
Potential applications of the Blockchain technology:
The current uses of the technology include thousands of cryptocurrencies that emerged after the success of Bitcoin. Private distribution ledgers are being employed by private companies to protect data but aren’t considered Blockchain technology by some as the essential feature of the Blockchain, its decentralised nature, isn’t available in these.
Smart contracts:
Perhaps, the most critical application of Blockchain yet, other than cryptocurrencies, is smart contracts, the electronic transaction protocols that execute on the fulfilment of specific condition without the need for human intervention. It is an extension of the application of cryptocurrency.
State, Administration, and Democracy:
Owing to its transparency and easy accessibility, the Blockchain could revolutionise governance if states come to embrace the technology; public availability of
democratic processes like elections, referendums, administrative contracts will enable that.
Protection of data and intellectual property:
As mentioned above, hacking of a decentralized peer-to-peer network is next to impossible. This will help in the protection of copyrights and other data.
File sharing:
Distributed ledger means data updated in the Blockchain gets disseminated throughout the network, speeding up the process of file sharing.
Stock markets and prediction:
Automated stock markets that pay out on meeting specific conditions will be a thing in the future with the advancement of Blockchain technology.
Agriculture:
blockchain technology can be and most probably will be effectively incorporated with agriculture as the practice gets automated in the future. The tech will enable recording various information needed for the practice that can be dispensed whenever and also establish a direct link between the producer and the consumer.
Thus, it is suffice to say that the onslaught of the new technology after having already revolutionized digital transactions will usher humanity into a new era; the possibilities of which are currently being explored.
Research Help GuideResearch Subject
Related Topics
Latest Research Topics
Gap analysis
Knowledge gap
PhD Guidance
PhD Help
PhD consultancy services
Research Article
 Previous Post
Previous Post Next Post
Next Post
