Cross-cultural Capabilities of Immigrant Entrepreneurs
Introduction
Across the globe, International migration has become a central characteristic of developing countries, contributing to the development of a multicultural and open society. The connection between international backgrounds and engagement in entrepreneurship are becoming more widely known, due to which the emergence of immigrant entrepreneurship has become a phenomenon of global importance (Morgan et al., 2018; Vahidnia et al., 2019).

Immigrant Entrepreneurship
Immigrant entrepreneurship has undergone significant change in the last few decades, prompting many scholars in the fields of management, economics, international business, entrepreneurship, and sociology to do extensive Research on this context (Ado et al., 2016). Further, it is noted that businesses developed by immigrants have adequate social and economic returns, including competitiveness, jobs, innovation, and prosperity, which in turn represents the Immigrant entrepreneurship success in different parts of the world (Carbonell et al., 2014). A recent conversation about the players involved in international entrepreneurship has helped to understand how immigrant entrepreneurs vary from other international entrepreneurs (Elo et al., 2018). Immigrant entrepreneurs are distinctive in their entrepreneurial internationalization approaches in relation to pathways and procedures, as a result of their unique capabilities, which assist them in bridging the capital from different countries (Vinogradov & Jorgensen, 2017).
Cross-Cultural Capabilities
In the immigrant entrepreneurship context, cross-cultural capabilities are defined as “the capability to handle uncertainty, a positive attitude, resilience, a developmental learning capability and a bilingual capability”. Cross-cultural adaptation refers to psychological and sociocultural adaptation in the field of immigrant entrepreneurship. That is, cross-cultural capabilities can be noted as skills of an individual relevant to psychological and sociocultural adaptation leveraged for business performance in home and host countries. Generally, a sociocultural adaptation capability describes the language skills, cultural learning, and bicultural flexibility of an individual. On the other hand, Psychological adaptation capability refers to managing emotions and the positive attitude of individuals (Kunlin Xu, 2017). The below figure represents the cross-cultural capabilities of immigrant entrepreneurship
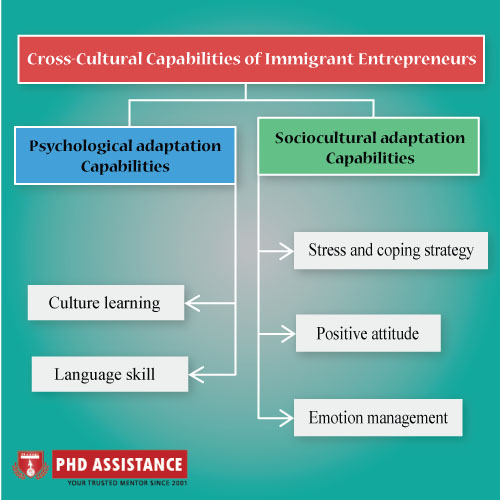
Figure 1: Cross-Cultural Capabilities of Immigrant Entrepreneurs
Conclusion
As a result, immigrant entrepreneurs must be able to transit between two cultural traditions, schemas, and behaviours in response to cultural prompts when they move to a foreign country with a different culture. Also, bicultural skills may be deemed more evident than multicultural capabilities to immigrant entrepreneurs because of the dual cultural environments in which they reside (Xu, 2021). In this view, cross-cultural capabilities of immigrant entrepreneurs are sets of skills linked with a socio-cultural and psychological adaptation of individual’s which can be used to improve outcomes for the business in both home and host countries. It is no doubt that Immigrant entrepreneurs will undeniably benefit from their cross-cultural skill.
References
Ado, A., Chrysostome, E., & Su, Z. (2016). Examining Adaptation Strategies of Sub-Saharan African Immigrant Entrepreneurs In China: The Case of Guangdong. Journal of Developmental Entrepreneurship, 21(04), 1650027. https://doi.org/10.1142/S1084946716500278
Carbonell, J. R., Hernandez, J. C. P., & García, F. J. L. (2014). Business creation by immigrant entrepreneurs in the valencian community. The influence of education. International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal, 10(2), 409–426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11365-011-0211-2
Elo, M., Sandberg, S., Servais, P., Basco, R., Cruz, A. D., Riddle, L., & Täube, F. (2018). Advancing the views on migrant and diaspora entrepreneurs in international entrepreneurship. Journal of International Entrepreneurship, 16(2), 119–133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10843-018-0231-x
Kunlin Xu. (2017). The importance of cross-cultural capabilities for Chinese immigrant entrepreneurs in Australia. Queensland University of Technology. https://eprints.qut.edu.au/110823
Morgan, H. M., Sui, S., & Baum, M. (2018). Are SMEs with immigrant owners exceptional exporters? Journal of Business Venturing, 33(3), 241–260. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0883902616301690
Vahidnia, H., Mitchell, J. R., Smith, J. B., Assaf, A. M., Mitchell, R. K., & Araci, O. (2019). Further exploring international entrepreneurial cognitions: The case of the Middle-East. Journal of Business Venturing Insights, 11, e00112. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352673418301112
Vinogradov, E., & Jorgensen, E. J. B. (2017). Differences in international opportunity identification between native and immigrant entrepreneurs. Journal of International Entrepreneurship, 15(2), 207–228. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10843-016-0197-5
Xu, K. (Linley). (2021). Cross-cultural Capabilities: Leveraging Cross-cultural Capabilities for Immigrant Entrepreneurs’ Performance. https://www.anzam.org/wp-content/uploads/pdf-manager/2624_171.PDF
 Previous Post
Previous Post Next Post
Next Post
