DeLone and McLean Information System Success Model
DeLone and McLean Information System Success Model
In 1992, DeLone and McLean [2003] inclusively examined IS success measures and developed a model of interrelationship that exist between the six IS success variable categories: ‘system quality’; ‘information quality’; ‘use’; ‘user satisfaction’; ‘individual impact’ and ‘organizational impact as depicted in the Figure 3.
Figure 3: Information System Success Model –
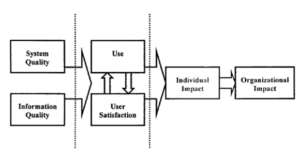
Adopted fromDeLone and McLean (1992)
The figure 3 presents the Information system Success model of Delone and McLean (1992). It was observed that the overall degree of system quality and information quality was associated with degree of use and user satisfaction. These two facets were most important in identifying the impact on an individual and the ultimate impact on an organization.
Later, DeLone & McLean [2003] presented an update to their IS success model. Figure 4 depicts theupdated model that focuses on the primary changes required considering the quality and service quality. They defined their model dimension as follows:
• Systems quality: It is determined by flexibility, accessibility, reliability, response rate and utility.
• Information quality: It is determined by integrity, capability of understanding, personalization, relevance and safety.
• Service quality: It is determined by commitment, sympathy and sensibility.
• Use: It is determined by nature of use, navigation patterns, traffic and number of executed transactions
• User satisfaction: It is determined by frequent purchases, frequent visits and user surveys
•Net benefits: These are measured by cost savings, market expansions, incremental additional sales, decreased search costs and time savings.
Figure 4: The updated DeLone and McLean’s 2003 Model
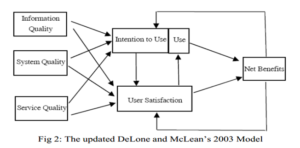
The figure 4 presents the updated Delone and McLean (2003) model which improved upon the Delone and McLean (1992) model. The main feature of this model included another factor impacting success of IS apart from Information and System quality which is the Service Quality. The intention to use and user satisfaction was found to have a direct relationship with the net benefit perceived. If the degree of net benefit was more than the degree of intention to use and user satisfaction was also more and vice versa.
A relatively high content in psychology has supported general motivation theory to describe behaviour. Vallerand (1997) introduced an exemplary review on the basic principles underlying the theoretical foundation. Likewise, Davis et al. (1992) enforced this theory to study new technology and usage. There are a number of studies supporting the updated DeLone and McLean (D&M) model. For organizations, either public or private to adopt e-services require huge investments that in turn, results in vast varieties of e-services in most countries.
It is also to be acknowledged that there is low usage failing the expectationlevel and frequent occurrence of problems (European Commission, 2005; Parasuraman et al., 2005; Sumak et al., 2009) and , a research was carried out for evaluating and quality checking of e-services. Nonetheless, the former discussed about the e-service success model, since, the present study assess the behaviour of citizens on e-service adoption, it would be appropriate to study the behaviour based theoretical models. The following section critically reviews the different adoption models.

